-
Products
-
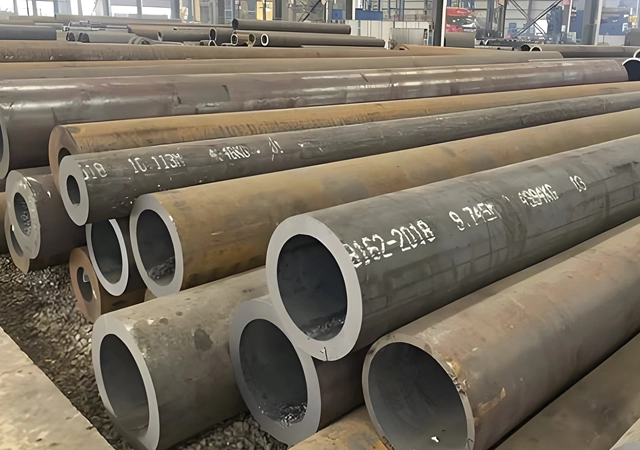
Seamless Steel Pipe/Tube
- Carbon Steel Seamless Pipe
- Boiler Steel Pipe
- Casing and Tubing
- Line Pipe
- Oil and Gas Pipeline
- Structural Steel Pipes
- Mechanical Steel Tubing
- Petroleum Cracking Pipe
- High-pressure Fertilizer Pipes
- Heat Exchanger Pipes
- Hydraulic Pillar Pipe
- Marine Seamless Pipe
- Geological Drilling Pipes
- Low-temperature Pipe
- High Pressure Steel Pipe
- High Temperature Pipe
- Hot Rolled Seamless Pipe
- Cold Drawn Seamless Pipe
- Pipe Fittings
- Flanges
- Valve
-
Seamless Steel Pipe/Tube
- Standard
- Application
- Company
- Resources
- Blog
- Contact Us
 EN
EN